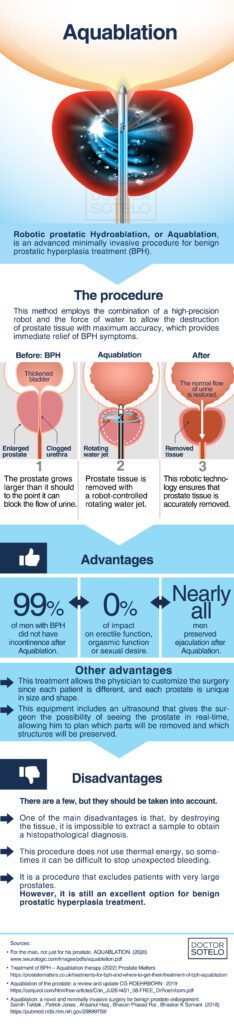
Robotic prostatic hydroablation, or Aquablation, is an advanced minimally invasive procedure for benign prostatic hyperplasia treatment.
This method employs the combination of a high-precision robot and the force of water to allow the destruction of prostate tissue with maximum accuracy, which provides immediate relief of symptoms.
Another advantage of this treatment is that it allows the physician to customize the surgery since each patient is different, and each prostate is unique in size and shape. This equipment includes an ultrasound that gives the surgeon the possibility of seeing the prostate in real- time, allowing him to plan which parts will be removed and which structures will be preserved; reducing complications such as erectile dysfunction, incontinence and preserving ejaculation.
As for the disadvantages, there are a few, but they should be taken into account. One of the main disadvantages is that, by destroying the tissue, it is impossible to extract a sample to obtain a histopathological diagnosis. Another disadvantage occurs because this procedure does not use thermal energy, so sometimes it can be difficult to stop unexpected bleeding. Finally, it is a procedure that excludes patients with very large prostates.
However, it is still an excellent option for benign prostatic hyperplasia treatment.
REFERENCES:
-For the man, not just for his prostate. AQUABLATION. (2020) PROCEPT BioRobotics Corporation. Documento en línea. Disponible: https://www.swurologic.com/images/pdfs/aquablation.pdf
-Treatment of BPH – Aquablation therapy (2022) Prostate Matters Documento en línea. Disponible: https://prostatematters.co.uk/treatments-for-bph-and-where- to-get-them/treatment-of-bph-aquablation/
– Aquablation of the prostate: a review and update CG ROEHRBORN · 2019 Documento en línea. Disponible: https://canjurol.com/html/free- articles/Cdn_JU26-I4S1_08.FREE_DrRoehrborn.pdf
-Aquablation: a novel and minimally invasive surgery for benign prostate enlargement. Samih Taktak , Patrick Jones , Ahsanul Haq , Bhavan Prasad Rai , Bhaskar K Somani (2018) Documento en línea. Disponible: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29899759/